TOPICS:American Geophysical UnionClimate ChangeGeophysicsOceanographyWater
ByAMERICAN GEOPHYSICAL UNIONJULY 2, 2021
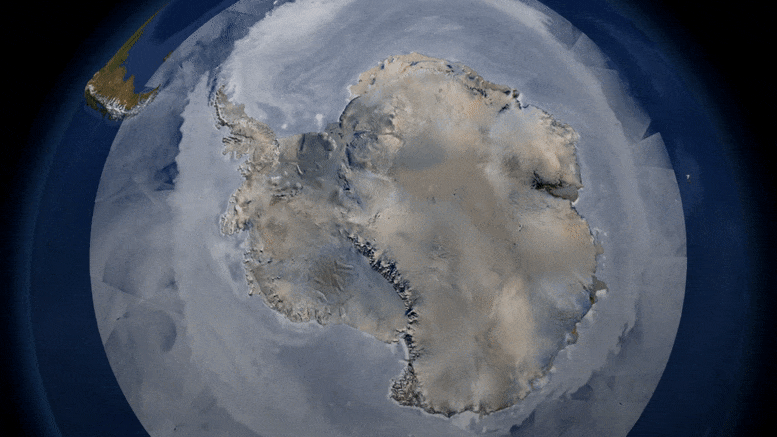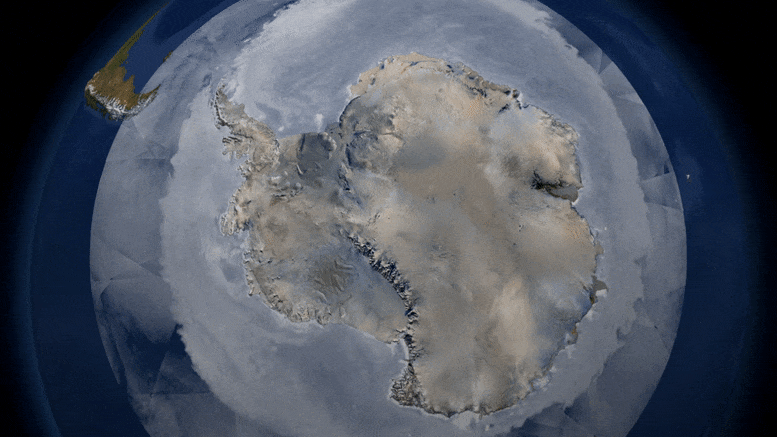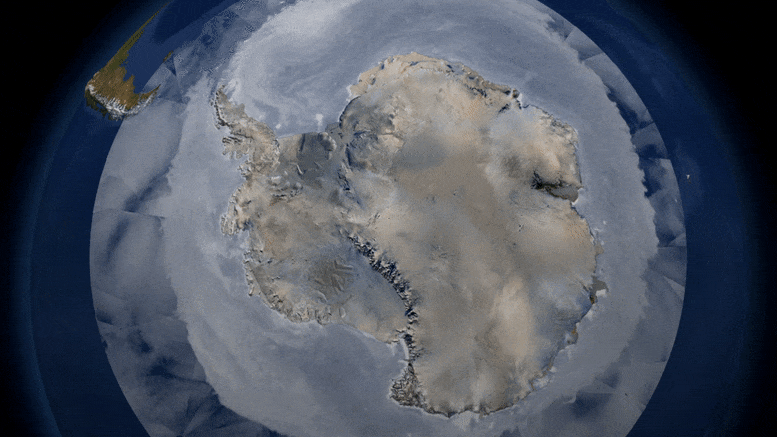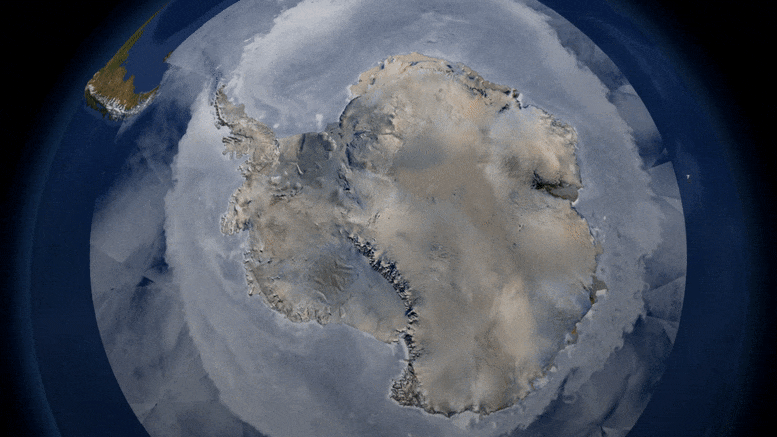
First global assessment of the extent of snow and ice cover on Earth’s surface—a critical factor cooling the planet through reflected sunlight—and its response to warming temperatures.
The global cryosphere—all of the areas with frozen water on Earth—shrank by about 87,000 square kilometers (about 33,000 square miles), a area about the size of Lake Superior, per year on average, between 1979 and 2016 as a result of climate change, according to a new study. This research is the first to make a global estimate of the surface area of the Earth covered by sea ice, snow cover, and frozen ground.
The extent of land covered by frozen water is just as important as its mass because the bright white surface reflects sunlight…
View original post 629 more words
