Stanford University / Phys.Org
June 1, 2020
See <https://phys.org/news/2020-06-loss-land-based-vertebrates.html> link
for photos.
In 2015, Stanford biologist Paul Ehrlich coauthored a study declaring the
world’s sixth mass extinction was underway. Five years later, Ehrlich and
colleagues at other institutions have a grim update: the extinction rate is
likely much higher than previously thought and is eroding nature’s ability
to provide vital services to people.
Their new paper, published this week in Proceedings of the National Academy
of Sciences, indicates the wildlife trade and other human impacts have wiped
out hundreds of species and pushed many more to the brink of extinction at
an unprecedented rate.
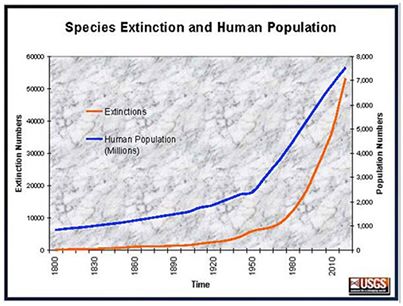
For perspective, scientists estimate that in the entire twentieth century,
at least 543 land vertebrate species went extinct. Ehrlich and his coauthors
estimate that nearly the same number of species are likely to go extinct in
the next two decades alone.
The trend’s cascading effects include an intensification of human health
threats, such as COVID-19, according to the researchers. “When humanity
exterminates populations and species of other creatures, it is sawing off
the limb on which it is sitting, destroying working parts of our own
life-support system,” said Ehrlich, the Bing Professor of Population
Studies, emeritus, at the Stanford School of Humanities and Sciences and a
senior fellow, emeritus, at the Stanford Woods Institute for the
Environment. “The conservation of endangered species should be elevated to a
national and global emergency for governments and institutions, equal to
climate disruption to which it is linked.”
The study comes in the wake of an April 7 letter from a bipartisan group of
senators urging the Trump administration to close markets that sell live
animals for food and unregulated wildlife markets, among other measures to
stop the trade in illegal wildlife and wildlife products.
Human pressures, such as population growth, habitat destruction, the
wildlife trade, pollution and climate change, critically threaten thousands
of species around the world. Ecosystems ranging from coral reefs and
mangrove forests to jungles and deserts depend on these species’
long-evolved relationships to maintain their functioning and make them
resilient to change. Without this robustness, ecosystems are less and less
able to preserve a stable climate, provide freshwater, pollinate crops and
protect humanity from natural disasters and disease.
Final Opportunity
To better understand the extinction crisis, the researchers looked at the
abundance and distribution of critically endangered species. They found that
515 species of terrestrial vertebrates- 1.7 percent of all the species they
analyzed- are on the brink of extinction, meaning they have fewer than 1,000
individuals remaining. About half of the species studied have fewer than 250
individuals left. Most of the highly endangered species are concentrated in
tropical and subtropical regions that are affected by human encroachment,
according to the study.
In addition to rising extinction rates, the cumulative loss of
populations-individual, localized groups of a particular species- and
geographic range has led to the extinction of more than 237,000 populations
of those 515 species since 1900, according to the researchers’ estimates.
With fewer populations, species are unable to serve their function in an
ecosystem, which can have rippling effects. For example, when overhunting of
sea otters-the main predator of kelp-eating sea urchins-led to kelp die-offs
in the 1700s, the kelp-eating sea cow went extinct.
“What we do to deal with the current extinction crisis in the next two
decades will define the fate of millions of species,” said study lead author
Gerardo Ceballos, a senior researcher at the National Autonomous University
of Mexico’s Institute of Ecology. “We are facing our final opportunity to
ensure that the many services nature provides us do not get irretrievably
sabotaged.”
The loss of endangered creatures could have a domino effect on other
species, according to the researchers. The vast majority-84 percent-of
species with populations under 5,000 live in the same areas as species with
populations under 1,000. This creates the conditions for a chain reaction in
which the extinction of one species destabilizes the ecosystem, putting
other species at higher risk of extinction.
“Extinction breeds extinction,” the study authors write. Because of this
threat, they call for all species with populations under 5,000 to be listed
as critically endangered on the International Union for Conservation of
Nature Red List, an international database used to inform conservation
action on a global scale.
Timely Implications
These findings could aid conservation efforts by highlighting the species
and geographic regions that require the most immediate attention.
Understanding what species are at risk can also help identify what factors
might be most responsible for rising extinction rates.
Among other actions, the researchers propose a global agreement to ban the
trade of wild species. They argue the illegal capture or hunting of wild
animals for food, pets and medicine is a fundamental ongoing threat not only
to species on the brink, but also to human health. COVID-19, which is
thought to have originated in bats and been transmitted to humans through
another creature in a live animal market, is an example of how the wildlife
trade can hurt humans, according to the researchers. They point out that
wild animals have transmitted many other infectious diseases to humans and
domestic animals in recent decades due to habitat encroachment and wildlife
harvesting for food.
“It’s up to us to decide what kind of a world we want to leave to coming
generations-a sustainable one, or a desolate one in which the civilization
we have built disintegrates rather than builds on past successes,” said
study coauthor Peter Raven, president emeritus of the Missouri Botanical
Garden.
<https://phys.org/news/2020-06-loss-land-based-vertebrates.html>
https://phys.org/news/2020-06-loss-land-based-vertebrates.html